Abdominal Paracentesis
Definition
Abdominal Paracentesis - needle drainage of fluid from abdominal cavity
Indications
to relieve abdominal pressure from ascites
to diagnose spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and other infections (e.g. abdominal TB)
to diagnose metastatic cancer
to diagnose blood in peritoneal space in trauma
Contraindications
Uncorrected bleeding diathesis
Previous abdominal surgeries with suspected adhesions
Severe bowel distention
Abdominal wall cellulitis at the proposed site of puncture
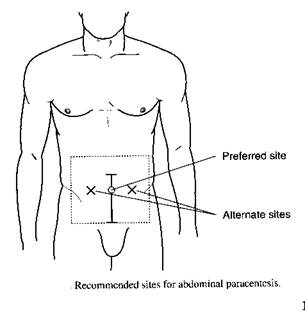
Site of puncture
Two centimeters below the umbilicus in the midline (through the linea alba)
Five centimeters superior and medial to the anterior superior iliac spines on either side
The Procedure
An out-patient procedure
a very small risk of introducing an infection, causing excessive bleeding or perforating a loop of bowel.
Patient lies down.
skin on the side of the abdomen is cleaned with an antiseptic solution
Local anesthesia admininstered
a fairly large-bore needle (along with a plastic sheath) is inserted 2 to 5 cm to reach the peritoneal (ascitic) fluid. The needle is then removed, leaving the plastic sheath behind to allow drainage of the fluid.
The fluid can be drained by gravity
Up to 10 litres of fluid may be drained during the procedure.
If fluid drainage is more than 5 litres, patients may receive intravenous serum albumin (25% albumin, 8g/L) to prevent hypotension
If the BP is normal after the procedure and the patient is asymptomatic the patient can go home.